BOOK CULTURE
This article examines the emergence and development of book history within the Western (primarily European and North American) academic landscape of the 20th century. The study aims to trace the key stages in the formation of book history as an interdisciplinary field, identifying major scholars and their research directions. The author explores the transition from early bibliographic studies to the establishment of an independent discipline that investigates social, economic, and cultural dimensions of text production, dissemination, and reception. The relevance of this research is driven by the growing interest in interdisciplinary approaches within the social and human sciences, which allow the consideration of the book not only as a text but also as a cultural artifact. Special attention is given to the contributions of key figures such as Lucien Febvre, Henri-Jean Martin, Donald Francis McKenzie, Roger Chartier, and Robert Darnton, whose ideas significantly influenced the development of interdisciplinary methods for analyzing the book as a unique cultural phenomenon. The study also examines fundamental theoretical models that explain the “life cycle” of the book—from its creation and publication to its reception and preservation. A distinct focus is placed on the emergence of book history research centers and scholarly societies, which played a crucial role in the institutionalization of this field in the 1980s and 1990s. The practical significance of this work lies in its potential application to educational programs in book history, cultural studies, and library science, as well as in the refinement of theoretical and methodological approaches for further research in the study of book culture.
The article is devoted to the analysis of the experience in preparing and publishing the biographical series of scientific monographs "National Heritage of Russia. Outstanding Scientists of the Urals" and "Creators of the Ural Industry" as tools for recording and popularizing the scientific and industrial heritage of the region. The need to document and perpetuate the achievements of scientists and industrial leaders who have made a significant contribution to the development of science and industry is driven by the growing interest in regional history and the demand for reliable biographical studies. The aim of the study is to explore the mechanisms of creating and implementing these series and to identify successful practices of collaboration between the scientific community, government structures, and industrial enterprises. The article analyzes the stages of monograph preparation, including work with various sources, expert involvement, and organizational aspects. The main results of the study include the systematization of accumulated experience, the assessment of the series’ contribution to the formation of a scientific information base on outstanding regional figures, and the determination of prospects for the further development of biographical research. The authors emphasize the importance of continuing the study and promotion of the scientific and industrial heritage of the Urals as a key factor in strengthening national identity and forming the country’s scientific elite.
The article examines current issues in the development of archaeography in Siberia, focusing on identifying Siberian manuscripts and collections within Moscow monasteries in the 19th and early 20th centuries, their circulation, and collection formation. The integration of Siberian culture into the panRussian context was significantly influenced by the personality and policies of ruling bishops. In the second half of the 19th century, this was Metropolitan Innocent (Veniaminov), who had Siberian origin and extensive service there. His activities as Metropolitan of Moscow facilitated the attraction of Siberian clergy to the capital, who brought their book and manuscript collections, which could be concentrated in specific Moscow Orthodox monasteries. The Pokrovsky Missionary Monastery, along with its affiliated Missionary Institute, could become a center for concentrating manuscripts and individual missionary artifacts. The article attempts to analyze the manuscript collection of Archpriest Fortunat Petukhov as a reflection of the institute's library formation. Using the manuscript collection of Archimandrite Philaret as an example, the article seeks to present the principles of collection formation, manuscript selection criteria, and raises the question of studying the activities of the institute's graduates in missions in Siberia, the Far East, and the Turkestan region. The institute's library, like its manuscript collection, requires research. The example of Moscow's Zlatoustovsky Monastery indicates that Siberian manuscripts could also enter monastic collections through donations from Siberian parishioners, thereby testifying to Siberian sacred sites (the life of St. Innocent of Irkutsk).
OVERVIEWS
The article is devoted to the review of modern research on the activities of public libraries on popularization and promotion the achievements of Russian science and technology. Based on the analysis of 35 publications (from the mid-2010s to the present), two main directions have been identified. The first one is represented by scientific researchs conducted by scientists from the St. Petersburg and Moscow State Institutes of Culture during the preparation of dissertations. They consider the popularization of science 1) as a tool for developing the scientific literacy of readers of mass libraries through the management of reading popular science literature, and 2) as a technology for digitalizing cultural and leisure activities. The second direction has begun to take shape in the 2020s at the State Public Scientific and Technological Library of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. It is focused on the development of popularization activities of libraries of different types and library promotion of scientific and technical achievements with the help of scientific and popular science literature and its reading management, non-book forms are given a supporting role. This area is being implemented as a scientific project. The research of the second direction is of a complex, fundamental nature. Historical, theoretical and methodological researches are aimed at reconstructing the history of the formation and development of the Soviet educational model of librarianship. It studies the evolution of state policy in the field of enlightenment in relation to librarianship, the development of the concept of library promotion of scientific knowledge, as well as the study and development of popularization activities of libraries in social media. Empirical research is aimed at studying modern libraries and their readers, as well as methodological support for the creation of recommendatory bibliographic resources. The article summarizes the study results of library role in science communication: it shows achievements and discussion aspects in modern researchers’ investigations, thus updating studies on this theme.
LIBRARY WORLD
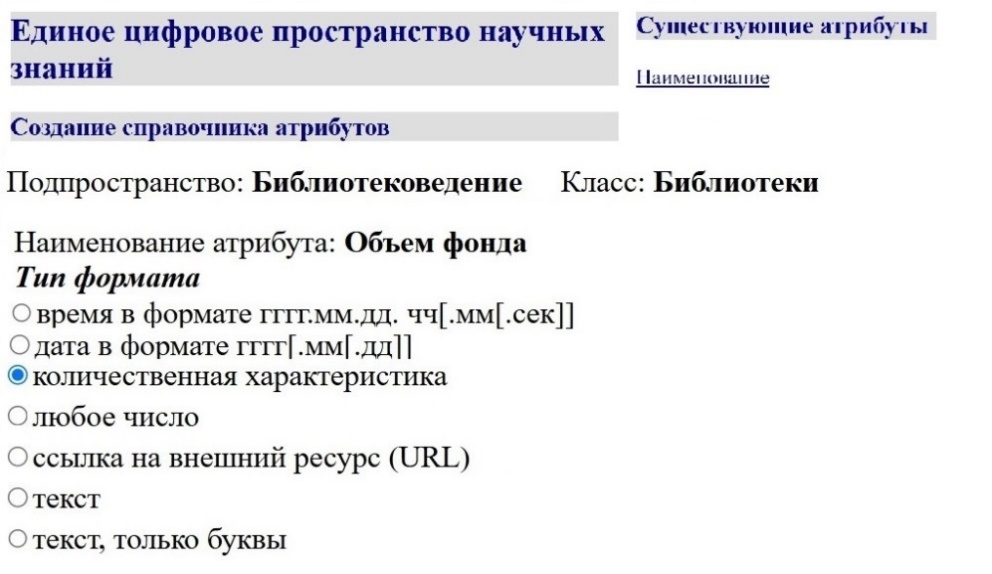
The article is dedicated to the problem of forming the Common Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge (CDSSK) content. CDSSK is a structured information environment that ensures the formation, storage, and provision of multi-species digital scientific information as linked data, the accuracy of hich is confirmed by the scientific community. CDSSK represents a combination of universal and thematic subspaces that reflect heterogeneous objects related to scientific knowledge. The object can be a digital copy of a physical entity (for example, a book, museum object, archival document, etc.), a database, information about an event, organization, scientific fact, etc. The article presents information about the current state of work in the field of forming the CDSSK and discusses issues related to the reflection of Library Science as a scientific field within the CDSSK. A variant of the structure of the subspace “Library Science” is proposed. It includes classes of objects such as “key concepts”, “persons”, “publications”, “documents”, “organizations”, and “scientific events”. The objects attributes of these classes and various types of relationships, including those with objects from other subspaces, are considered.
The development of digital technologies necessitates the adaptation of libraries to the conditions of the modern information society. Their key task is to provide users with constant round-the-clock access to information resources and services, regardless of the time constraints of the traditional work schedule. In the field of library and information services, there is an increasing trend towards the introduction of digital tools – chat-bots and dialog agents, operating on the basis of artificial intelligence and providing operational user service in real time. This article examines the evolution of chatbots, analyzes their functional features, and identifies areas of use in the field of library and information services, with an emphasis on reference services focused on meeting the information needs of library users. Attention is paid to the terminological aspect; it is noted that the generally accepted definition of the term “chat-bot” has not yet been developed. An analysis of the advantages of using chat-bots in the library is given, the main of which are ensuring round-the-clock availability of information services, including at night, and reducing the burden on library staff. The author of the article concludes that the development of chat-bots based on artificial intelligence is promising and necessary to improve the efficiency of library and information services. However, despite the obvious advantages, the introduction of chat-bots in library and information services involves a number of conditions and risks. The conditions include the need to carefully select a platform and develop scenarios for interacting with users, as well as constant training and updating of the chat-bot’s knowledge base. Risks include the possibility of incorrect interpretation of user requests, the provision of inaccurate or outdated information, as well as issues related to data confidentiality. For the successful implementation of chatbots, it is necessary to take these factors into account and develop a strategy aimed at minimizing risks and ensuring high-quality service.
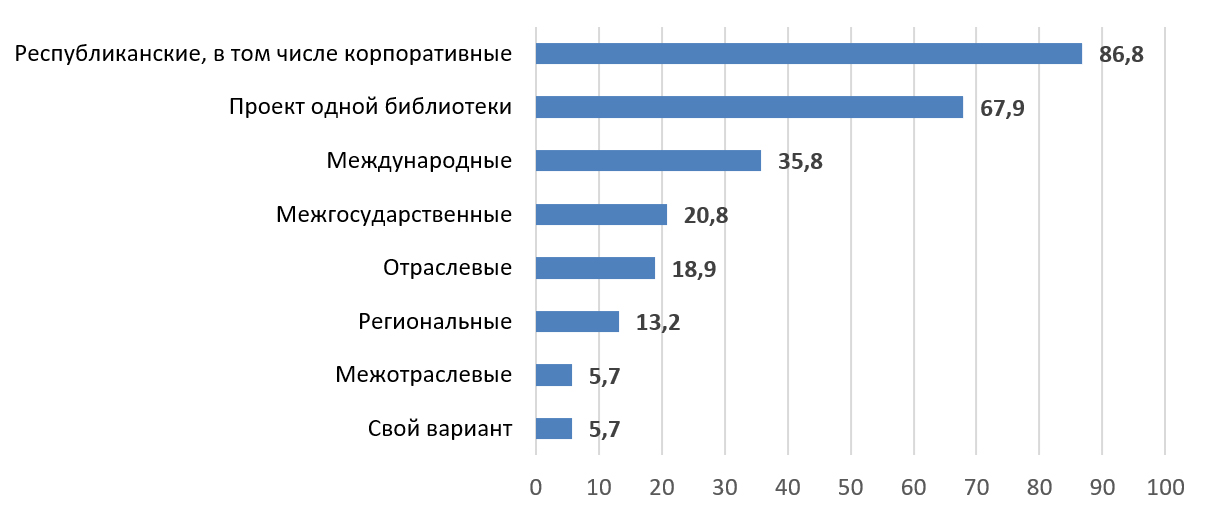
The article is devoted to the analysis of the innovative and managerial potential of the project activities of scientific libraries, which is a complex and multi-component area of work. The author considers key aspects of the success of this activity: knowledge-competence, organizational and reflexive, physiological and psycho-emotional. The importance of conditions that contribute to the effectiveness of the project work of scientific libraries, such as planning, team organization, control and the use of modern technologies is shown. The author offers interpretations of the definitions of the sphere of project activities of scientific libraries, such as “project in a scientific library”, “design in a scientific library”, “project activities of scientific libraries”, “library project management”, as well as the characteristics, methods and tools most often used in the project activities of scientific libraries. Particular attention is paid to the role of libraries in creating an information infrastructure, supporting scientific activities and professional training of personnel. The article presents the results of a sociological study of specialists from scientific libraries of Belarus involved in the development and implementation of projects. Based on empirical data, the features of project activities in republican and university libraries are revealed, criteria and factors of success that confirm the benefits of effective use of methods and tools, and demonstrate the high potential of project activities of libraries and the possibilities of its further development, are identified. The scientific novelty of the study lies in the fact that for the first time in Belarusian library science, theoretical and organizational issues of project activities are comprehensively substantiated with the account of typological specificity of a scientific library, due to the etymological unity with science and education. The results obtained can be useful for developing strategies to improve the effectiveness of project activities in scientific libraries.
The relevance of the topic discussed in the paper is due to the tasks set within the framework of the state cultural policy for libraries to transfer funds to digital format. The activities of regional libraries in this area are conducted according to two scenarios. The first one is the transfer of digital copies of rare and valuable publications that are missing in the collections of other institutions to electronic libraries at the federal level and above all to the National Electronic Library of the Russian Federation (NEL). As part of the second one, regional libraries form their own electronic collections and display either the full texts or information on possibilities of accessing them on official websites. The problem is there are different approaches to understanding the importance of this activity area. The purpose of the paper is to identify differences and evaluate the interim results of the work of regional libraries in the field of creating their own electronic resources and the conditions for providing them to their readers. The article collects and presents the table of statistical data on the number of digital copies of publications transferred to the NEL and on independently created electronic resources in regional libraries of the South of Russia. A comparative analysis of different libraries activity in this area is carried out. Newly formed electronic libraries differ in structure, volume of digitized publications, subject matter, and reference equipment. The results of the research can significantly complement the theoretical sections of the currently emerging electronic library science, and provide practical assistance to library institutions in solving the issues of unification of electronic libraries, achieving a balance of their quantitative, substantive and type-specific content. It is important for the successful solution of the tasks within the framework of the state regional cultural policy.
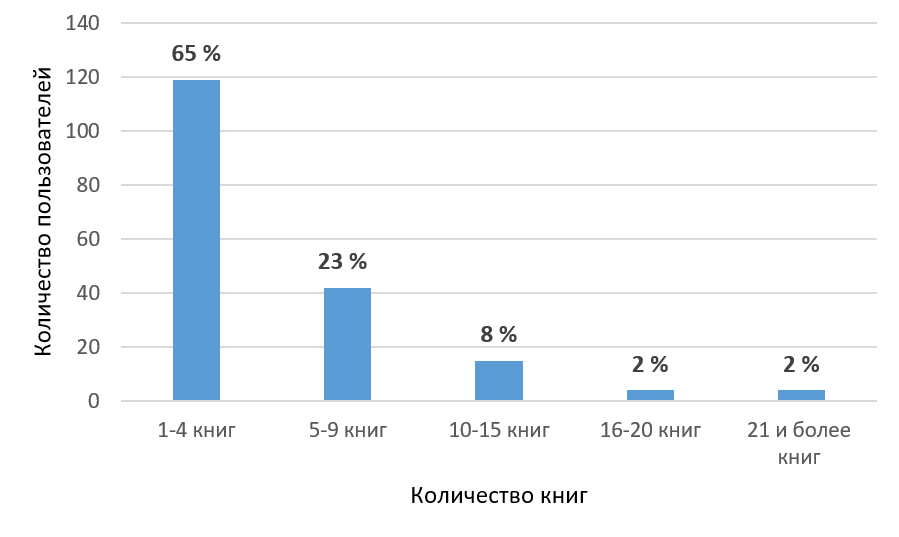
In the context of the increasing of information flow, the creation of bibliographic resources for the dissemination of scientific data is becoming especially relevant. It is important not only to collect and systematize information for specialists, but also to promote the involvement of a wide range of users in the process of obtaining new knowledge, to form a complete understanding of current research and its application in real life. The principle of personalization, based on individual needs and preferences, plays a key role in this process, allows the identification of relevant and useful information sources, and facilitation of the access to the necessary data for a wide audience. Bibliographic resources, in the preparation of which this principle is laid down, are becoming an important tool for supporting communication between science and society. The purpose of the article is to substantiate the importance of creating bibliographic resources taking into account the principle of personalization, which consists in adapting the content and functionality of resources to the individual needs, preferences and interests of users. The advantages of personalized bibliographic resources are highlighted: they can act as both scientific and advisory ones to support the process of interaction between science and society. The article presents the results of a study of individual needs and preferences in the field of popular science literature of 184 users of the State Public Scientific and Technical Library of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences based on the analysis of their electronic forms. The article shows the specific features of a bibliographer’s activities in creating personalized bibliographic resources for the dissemination of scientific knowledge in society.
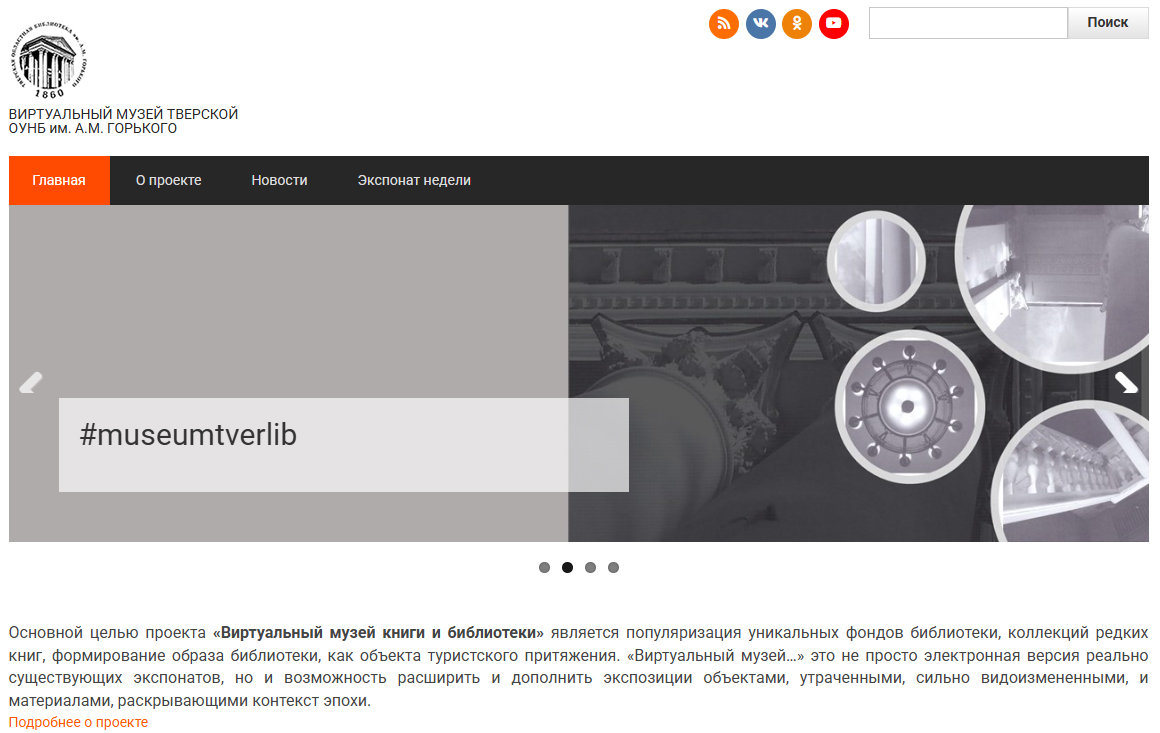
Virtual museums are a promising form of disclosure and popularization of unique book collections. The purpose of the study of the websites of central regional libraries in 2025 was to identify the best library practices in organizing digital resources. The number of virtual museums identified shows that libraries do not use this form as often one. The analysis is carried out taking into account the necessary components. They are the disclosure of document collections, the content of exhibitions, the quality of content, the convenience of the interface, navigation, meeting the information needs of various categories of users and allowed us to identify a number of central regional libraries using the form of a virtual museum to systematize and disseminate documented information of historical and cultural heritage. Due to the varying understanding of the definition of “virtual museum”, libraries organize online exhibitions in different ways, using different technological models and approaches to the formation of the site structure. Therefore, in some cases, the form of a virtual museum is indistinctly felt, the boundaries between a virtual library museum and thematic sites, electronic collections, and Internet encyclopedias become blurred. The general trends in the development of virtual museums, the relevance and potential of their development are shown, successful practices and their features are noted, an attempt is made to typologize the identified museums, key problems and challenges are identified. Many Russian libraries have the prospect of creating virtual museums, as they actually carry out museum and exhibition activities. This is possible under the condition of the development of project activities, a creative and competent approach to the development of the exposition plan, the right choice of technological solutions, and the organization of social partnership. Through virtual museums, it is possible to solve the tasks of disclosing funds and ensuring citizens’ access to cultural values regardless of their place of residence, maintain inclusivity and adapt different audiences to receive socially significant information.
In the context of the development of the knowledge society, obtaining reliable, high-quality information is becoming an important task. The library can fully implement this need. The practice of popularizing scientific knowledge, inherited by modern libraries from the Soviet model of librarianship, continues to be a key area of their activities. Exhibitions, lectures, seminars and other events are organized to attract readers’ attention to scientific content. The purpose of the article is to summarize the activities aimed at popularizing scientific and popular science knowledge in the national libraries of the CIS. The official library websites have served as a source. The conducted analysis have allowed the conclution that the activities to disseminate scientific knowledge are carried out at a high level in the national libraries of Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan. Events are held with the involvement of scientists and specialists, but rarely and irregularly. The activities of libraries in this direction should be continued, which is due, firstly, to the rapid growth of the volume of information and the need to verify it. Secondly, library collections are an effective tool against the dissemination of false information, as they are equipped with publications that have undergone scientific peer review, which eliminates the dissemination of fake information. In addition, the library is accessible to all segments of society and remains a free cultural institution.
SCIENCE IN FIGURES
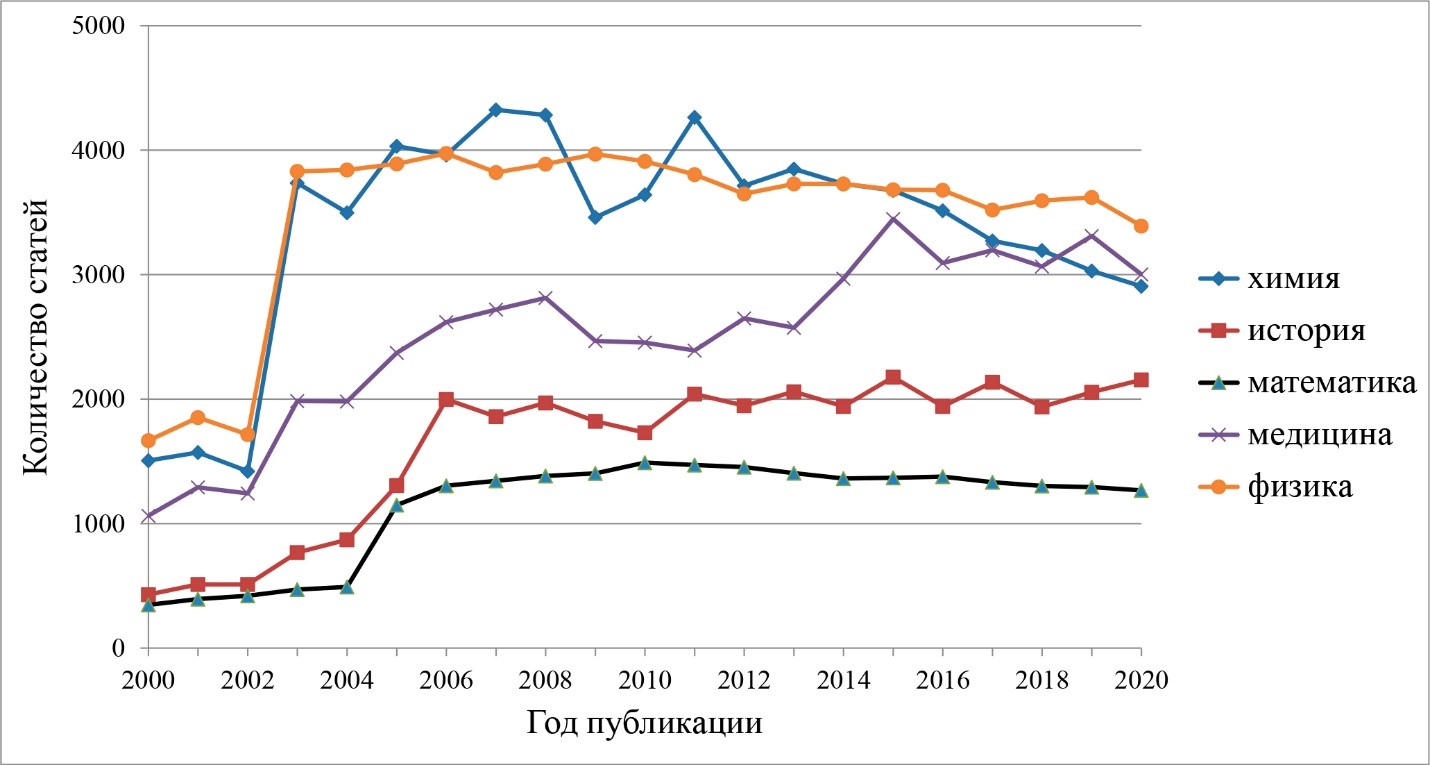
Scientific co-authorship is a natural reflection of the scientific collaboration. Multiple foreign studies based on Web of Science and Scopus data show that there has been an increase in the number of co-authors of scientific publications in international journals in various scientific areas over the recent decades. Obviously, it is rather difficult to perform an analysis of co-authorship in Russian journals using Web of Science and Scopus data. This paper examines trends in the number of co-authors of Russian scientific journal articles in the following five thematic areas: chemistry, history, mathematics, medicine, and physics. The data source of our investigation is the national bibliographic database Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI). We show a steady increase in the average number of co-authors per publication and an increase in the proportion of co-authored articles for the period from 2000 to 2020, and we notice differences in different scientific areas.
ISSN 2712-7931 (Online)