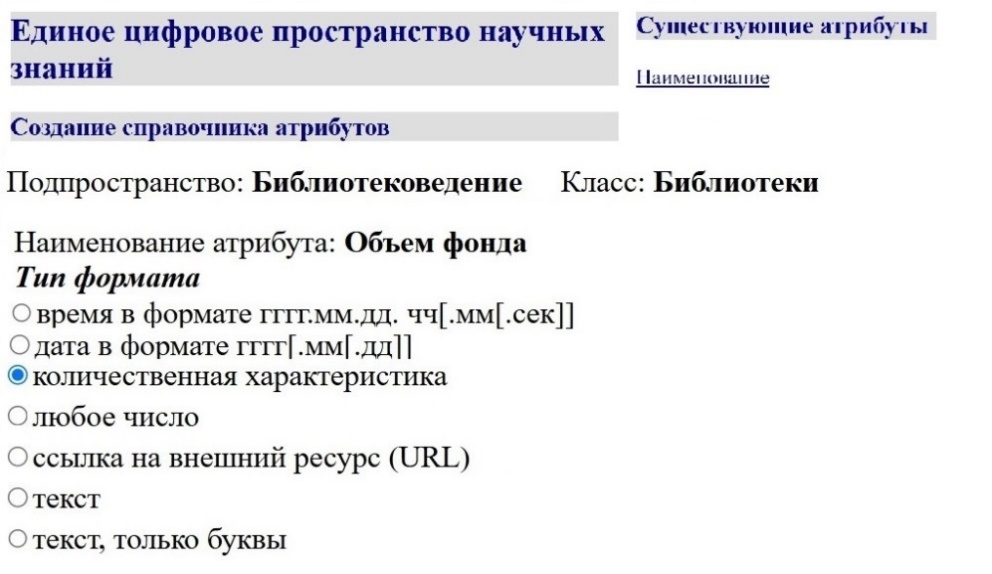
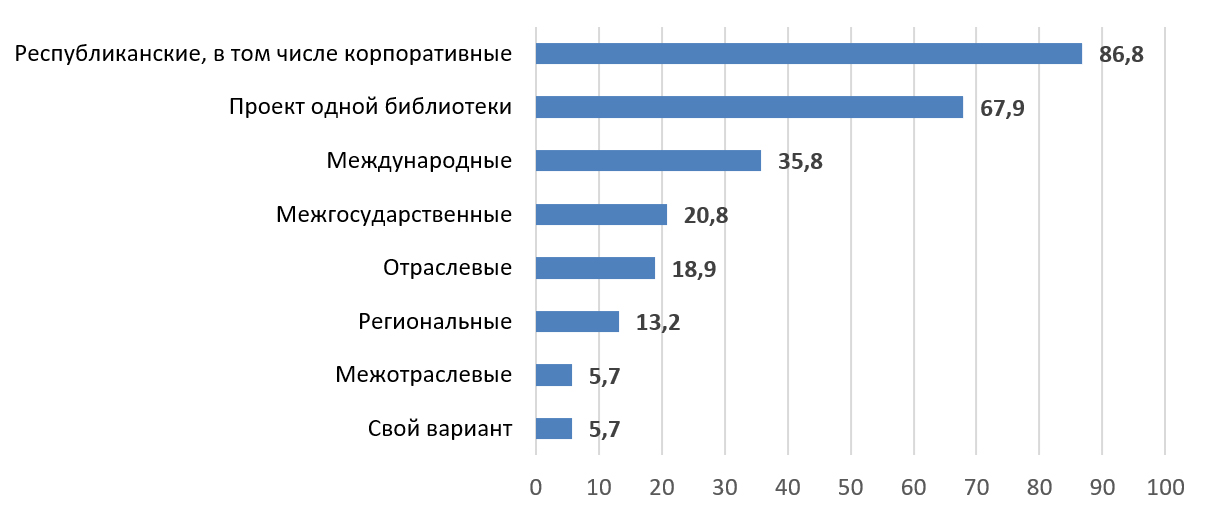
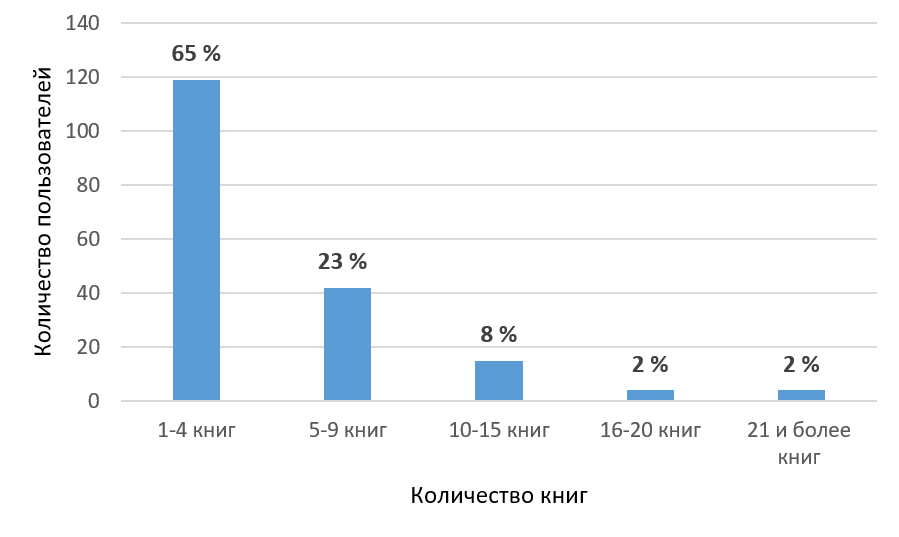
The Journal was founded by the State Public Scientific and Technological library of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (SB RAS) – the largest scientific library behind the Urals – and stated on the 23th of September 2004 by SB RAS’ Presidium. It was the first scientific journal on library science, bibliography science, book science, library informatics, results obtained with the help of bibliometric and scientomentric methods.
To determine the Journal policy and to peer review papers the Scientific-editorial Council was created, consisting of doctors of sciences and affiliated in research institutions, libraries, and universities of Russia and abroad, as well as the editorial board. In 2017 the Scientific-editorial Council and the editorial board were reorganized in the one board – editorial board with doctors of sciences and PhDs affiliated in research institutions, libraries, and universities of Russia and abroad.
The goal of the journal is to present the results of fundamental and applied investigations, advanced experience, as well as the research results obtained by scientometric and bibliometric methods. It publishes original research articles, surveys and discussions, as well as reviews on monographs and text-books worth of attention. Different types of information (about books-in-print, conferences, seminars, etc.) can be also found here. All materials are published free of charge. The journal published articles in Russian and English.
The journal entered the RISC core.
Chief editor (since 2016) is O. L. Lavrik, Dr. Ped. Sciences, professor, the head of laboratory of information and system analysis, affiliated in SPSTL SB RAS.
Currently, all issues of the Journal (since 2005) are available in e-format at this very site. Full texts are also open to readers in the Russian Index of Scientific Citation (elibary.ru, Cyberleninka. Each article has DOI.
Abstracts of each publications of the Journal appear in VINITI’s data base “Informatics”.
According to “The Law on a Legal Deposit Copy of Materials”, the journal printed copies are sent to the All- Russia Book Chamber and available in libraries receiving obligatory copies.